SAP ABAP Structure
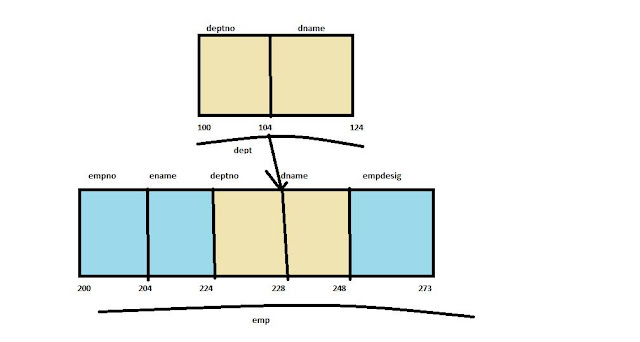 |
| Dept-Departmetn, Emp-Employee, Desig-Designation |
STRUCTURES: (WORK AREA / LINE TYPE / ROW TYPE)
è It is a user
defined data type which is a collection of different types of fields.
è In structures
the memory allocation is continuous. All the fields are stored one after the
other.
è The size of
the structure is equal to sum of the sizes occupied by structure fields.
è We can access
the structure fields by using structure name.
SYNTAX 1:
DATA: BEGIN OF
<STRUCTURE NAME>,
FIELD 1,
FIELD 2,
------------,
FIELD N,
END OF <STRUCTURE
NAME>.
Structure can store only one record.
è We use
structures whenever we need to capture interrelated information in the form of
a record.
Eg: employee à empno, ename,
empdesig, empsal…..
student à studentid, student name,
student addr…..
bank à bank accno, bank
acc.holder name, accholder addr….
Sales order à
salesperson,salesorderdate,createdby
è By default,
structure fields are initialized to respective default values based on the data
types.
è At any point
of time a structure can store only single record.
COPYING DATA BETWEEN TWO STRUCTURES:
è We can copy
the data of one structure to another structure by using assignment operator,
move and move-corresponding statements.
è In case of
assignment (=) and move statement, it only checks for corresponding data types
of the fields and not for names and the no of fields. If any one of the
corresponding field data type is not matching it leads to syntax error.
MOVE CORRESPONDING:
It is used to copy the data
between dis-similar structures.
It is recommended not to
use the move-corresponding statement because of the following 2 reasons.
è It decreases
the performance, because each field of the source structure is compared with
all the fields of the target structure which is time consuming and thereby
decreases the performance.
è It may lead to
run-time error i.e. While copying the data between two fields it only checks
for field’s names but not for data types. If data types are not type compatible
it leads to run-time error.
Nested structure:
Declaring a structure inside another structure.
Syntax:
Data : begin of <structure name1>, à outer
structure
Field 1,
Field 2,--------,
Begin of <structurename2>, à inner structure
Fields,
Field 2,
--- ---
End of
<structurename2>,
End of <structurename1>.
Accessing outer structure fields
<outer structure> - <field name>
Accessing inner structure fields
<outer structure> - <inner structure> - <field name>
Including Structures inside other structure
Note: We can include one
structure inside another structure by using ‘include structure’ (or) ‘include
type’ statement. The included structure can be local structure (available in
same object) or a global structure defined in the database.
Standard syntax for declaring structure:
1.
Create ‘Types’ declaration with the required
fields
Syntax:
Types: begin of <type name>,
Field 1,
Field 2,
--- --- --
Field n,
End of <type name>.
Note: ‘Types’
declaration doesn’t allocate any memory; it only provides the template of the
fields (field names and their data types). Types keyword is used for creating
user-defined data type.
2.
Based on Types declaration, we can create ‘n’ no.
of instances (structures/work areas)
Syntax:
Data <structure name> type <type
name>.
Note:- If anybody want some example of these all topic then kindly send/comment your mail id, i will send the all examples through mail in word format.
**Kindly like and share these all topic with your friends**


0 Comments